The aim of TT2 is to develop a Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) system, which will help to meet the growing demand for high-quality translation. The innovative solution proposed by TT2 is to embed a data-driven machine translation engine with an interactive translation environment. In this way, the system combines the best of two paradigms: the CAT paradigm, in which the human translator ensures high-quality output; and the MT paradigm, in which the machine ensures significant productivity gains. Another innovative feature of TT2 is that it will have two input modalities: text and speech. Six different versions of the system will be developed for English, French, Spanish and German. To ensure that TT2 corresponds to the translators' needs, two professional translation agencies will evaluate successive prototypes.
Project partners: SEMA Group, Lehrstuhl für Informatik VI, Computer Science Department, RWTH Aachen - University of Technology, Instituto Tecnologico de Informatica, RALI Laboratory - University of Montreal, Celer Soluciones, Societe Gamma, Xerox Research Centre Europe
The objective of the LC-STAR is to improve human-to-human and man-machine communication in multilingual environments. The project aims to create lexica and corpora needed for speech-to-speech translation. Within LC-STAR, quasi industrial standards for those language resources will be established, lexica for 12 languages and text corpora for 3 languages will be created. A speech to speech translation demonstrator for the three languages English, Spanish and Catalan will be developed. The Lehrstuhl für Informatik VI will focus on the investigation of speech centered translation technologies focusing on requirements concerning language resources and the creation of lexica for speech recognition in German.
LC-STAR is supported by the European Union. Project partners are Siemens AG (Germany), IBM Deutschland Entwicklung GmbH (Germany), Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya (Spain), NSC - Natural Speech Communication Ltd. (Israel), and Nokia Corporation (Finland).
The RWTH IRMA project is a joint project of the Institute of Medical Informatics, the Department of Diagnostic Radiology, and Lehrstuhl für Informatik VI. The goal of this project is the realization of a content-based image retrieval system suited for use in daily medical routine.
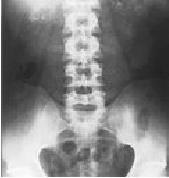
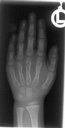
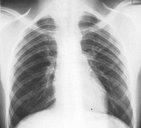
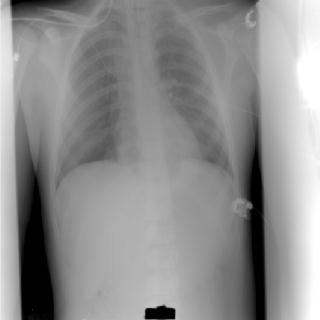
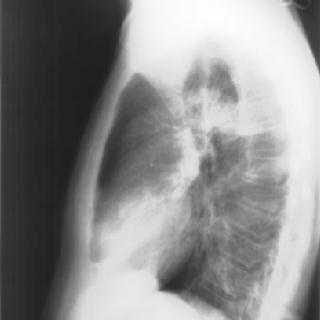
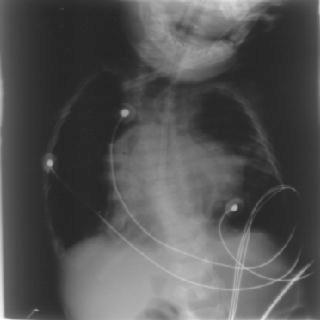
Examples from the IRMA database
Nowadays commercial speech recognition systems work well for a very specific task and language. However, they are not able to adapt to new domains, acoustic environments and languages. The objectives of the CORETEX project are to develop generic speech recognition technology that works well for a wide range of tasks with essentially no exposure to task specific data and to develop methods for rapid porting to new domains and languages with limited, inaccurately or untranscribed training data. Another objective is to investigate techniques to produce an enriched symbolic speech transcription with extra information for higher level (symbolic) processing and to explore methods to use contemporary and/or topic-related texts to improve language models, and for automatic pronunciation generation for vocabulary extension.
We began with first investigations in unsupervised training, i.e. train a speech recognition system for a new task without dedicated transcribed training data for this specific task. One problem with genericity and portability is the recognition vocabulary. When shifting to a new task, a lot of work has to be done to manually build phonetic transcriptions for new words. We developed a method for automatically determine the phonetic transcription (see section Pronunciation Modeling). Further we build a system to segment recorded broadcast shows into parts which can be handled by the speech recognition system.