Bits are transmitted as pulses, at about 69% the speed of light.


Bits are transmitted as pulses, at about 69% the speed of light.

Each has about 25 terahertz of capacity. So aggregate capacity could be 50-75 terabits.
-----------------------------------------------------
Data Rate SONET (US) CCITT (International)
(Mbits/sec) Designation Designation
-----------------------------------------------------
51.84 OC-1 -
155.52 OC-3 STM-1
622.08 OC-12 STM-4
1224.16 OC-24 STM-8
2488.32 OC-48 STM-16
-----------------------------------------------------
Solution: use multiple transmitters/receivers with different wavelengths.
D (Delta) channel: 16 kbps
Primary Rate: 23 B-channels and one D-channel in U.S. and Japan; 30 B-channels and two D-channels in Europe
ADSL is not about line, it is about the two modems at each end.
Name Meaning Data Rate Mode
_______________________________________________________________________
V.32 Voice Band Modems 1200 bps to Duplex
V.34 28,800 bps
DSL Digital Subscriber 160 kbps1 Duplex
Line
HDSL High Data Rate Digital 1.544 Mbps Duplex
Subscriber Line 2.048 Mbps Duplex
ADSL Asymmetric Digital 1.5 to 9 Mbps Down2
Subscriber Line 16 to 640 kbps Up
VDSL Very high data rate 13 to 52 Mbps Down
Digital Subscriber 1.5 to 2.3 Mbps Up3
Line
_______________________________________________________________________
1. 160 Kbps divides into two ISDN B channels (64 kbps), one D channel
(16 kbps) and link administration.
2. "Down" means downstream, from the network to the subscriber.
"Up" means upstream.
3. Future VDSL systems may have upstream rates equal to downstream,
but on much shorter lines.
Up to 18,000 feet 1.544 Mbps (T1)
16,000 feet 2.048 Mbps (E1)
12,000 feet 6.312 Mbps (T2)
9,000 feet 8.448 Mbps
OSI ATM ATM
Layer Layer Sublayer Functionality
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CS Interface (convergence), services to different applications
3/4 AAL - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
SAR cell/packet segmentation and reassembly
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Flow control
2/3 ATM Cell header generation/extraction
Virtual circuit / virtual path management
Cell multiplexing/demultiplexing
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cell rate decoupling
Header error checking (checksum)
2 TC Cell generation
Packing/unpacking cells
Frame generation
- - Physical - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Bit timing
1 PMD
Physical network access
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AAL -- ATM Adaptation Layer
CS -- Convergence Sublayer
SAR -- Segmentation And Reassembly sublayer
TC -- Transmission Convergence sublayer
PMD -- Physical Medium Dependent sublayer
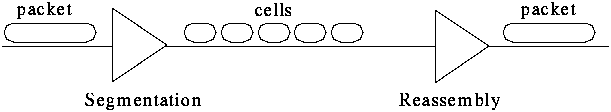
Chips are available to segment and reassemble (SAR chips)
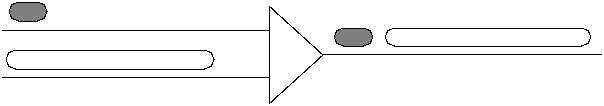
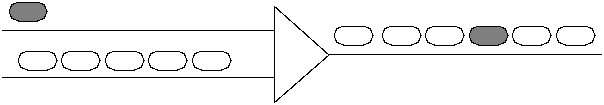
Increases speed of store-and-forward networks (it takes about 1 microsecond to receive a 128 byte cell on a 1 Gbit network).


VCI + VPI = unique routing indicator for the cell.
Like phone number, VPI is like area code (604), VCI is like phone number (555-1212)
Routers can use hop-by-hop routing, may route only on VPI in the network backbone.
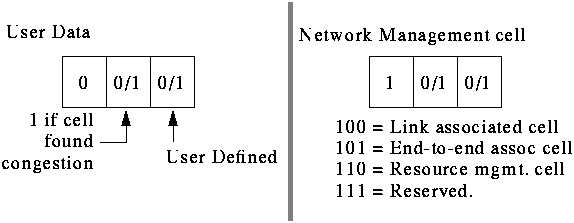
CLP = Cell Loss Priority. 1 - low priority, 0 - high priority (a hint for switches as to which cell to drop)
CRC = Cyclic Redundancy Code -- used for header error detection and correction
Top | Chap 5 | CMPT 365 Home Page | CS