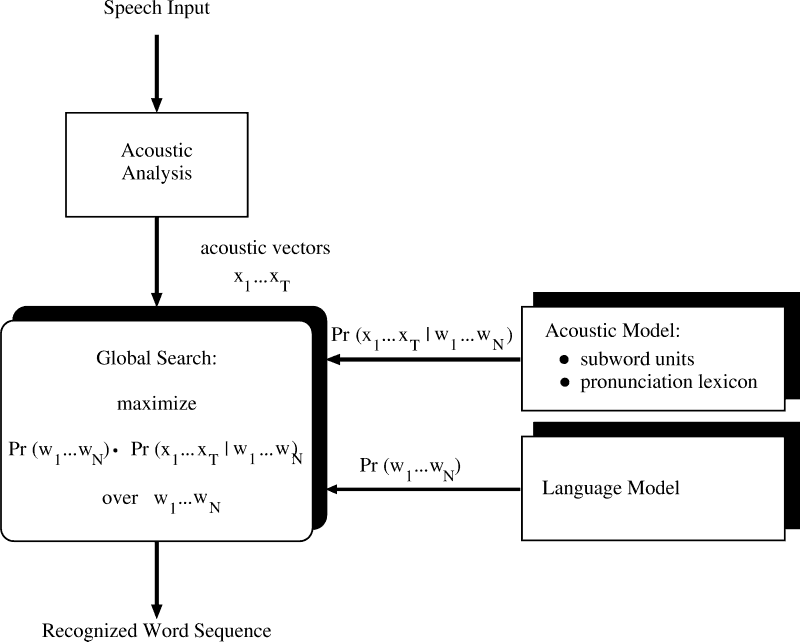
 Architecture of an automatic speech recognition system
Architecture of an automatic speech recognition system
Today, state-of-the-art systems for automatic speech recognition are
based on the statistical approach of Bayes decision rule. The
implementation of Bayes decision rule for automatic speech
recognition is based on two kinds of stochastic models: the acoustic
model and the language model which together are the basis for the
decision process itself, i.e. the search
for the most probable sentence. These modules of an automatic speech
recognition system are characterized as follows:
- The acoustic model captures the acoustic properties of
speech and provides the probability of the observed acoustic
signal given a hypothesized word sequence. The acoustic model
includes:
- The acoustic analysis
which parameterizes the speech input into a sequence of acoustic
vectors.
- Acoustic models for the
smallest sub-word units, i.e. phonemes which usually are
modelled context dependent.
-
The pronunciation lexicon, which defines the decomposition of
the words into the subword units.
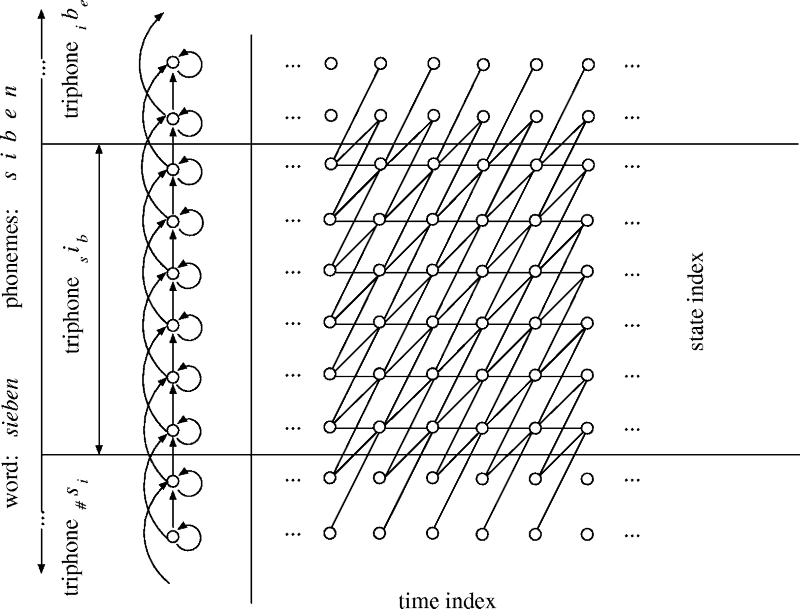 Topology and search space for a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) for the word "sieben"
Topology and search space for a Hidden Markov Model (HMM) for the word "sieben"
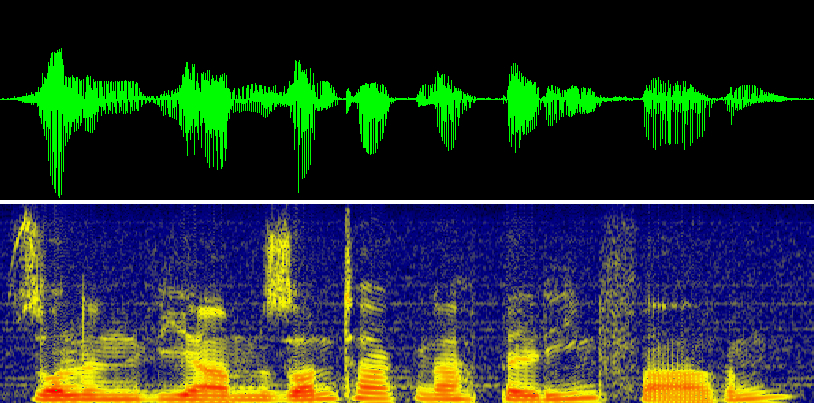 Speech waveform of the utterance "Sollen wir am Sonntag nach
Berlin fahren", and the corresponding FFT spectrum
Speech waveform of the utterance "Sollen wir am Sonntag nach
Berlin fahren", and the corresponding FFT spectrum
-
The language model captures the linguistic
properties of the language and provides the a-priori probability
of a word sequence. From an information theoretic point of view,
syntax, semantics, and pragmatics of the language could also be
viewed as redundancies. Because of the stochastic nature of such
redundancies, language models usually are based on
statistical concepts.
-
Search realizes Bayes decision criterion on the basis
of the acoustic model and the language model. This requires the
generation and scoring of competing sentence hypotheses. To
obtain the final recognition result, the main objective then is
to search for that sentence hypothesis with the best score using
dynamic programming. The efficiency of the search process is
increased by pruning unlikely hypotheses as early as possible
during dynamic programming without affecting the recognition
performance.



