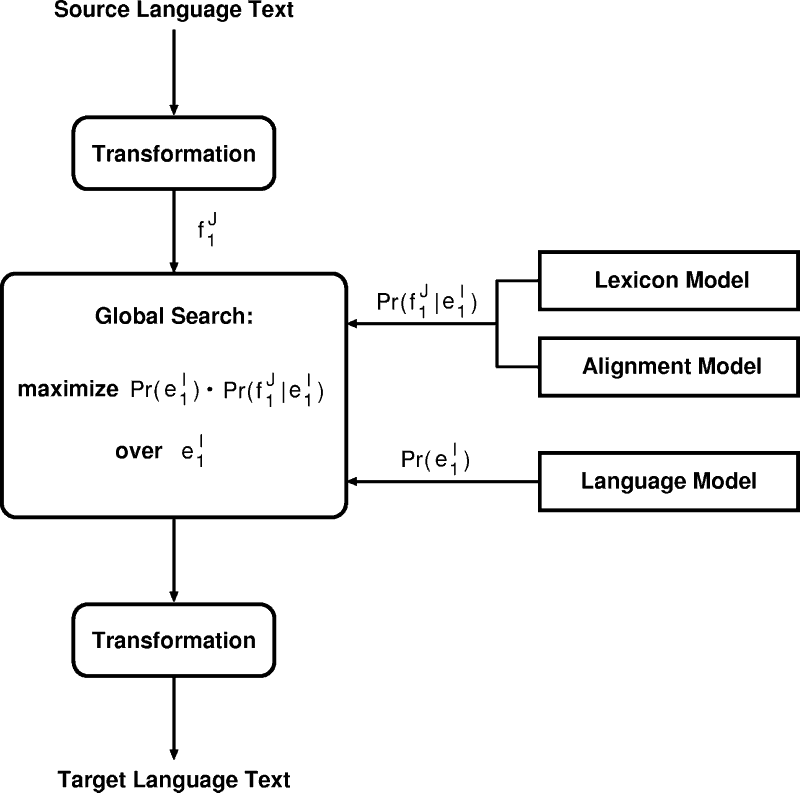
 Architecture of a Statistical Machine Translation System
Architecture of a Statistical Machine Translation System
The goal of machine translation is the translation of a
text given in some natural source language into a natural target
language. The input can be either a written sentence or a spoken
sentence that was recognized by a speech recognition system. At the Lehrstuhl für Informatik VI, we apply
statistical methods similar to those in speech
recognition. Stochastic models describe the structure of the sentences
of the target language - the language model - and
the dependencies between
words of the source and the target language - the translation model (see figure).
The translation model is decomposed into the
lexicon model which determines the translations of the words in
the source language and the alignment model forming a mapping
between the words in the source language string and the words in the
target language string.
These models are trained automatically on a
corpus of bilingual source/target sentence pairs.
In this approach, it is not necessary to manually design rules for the
translation or the construction of sentences.
A search algorithm determines the target language sentence that has
the highest probability given the source language sentence.
The statistical approach to machine translation is particularly
suitable for the translation of spontaneous speech, where the
translation approach has to cope with colloquial language and speech
recognition errors.

